Overview
Some of the largest corporations use cloud technology, and its popularity makes sense. It can deliver various services through the internet; all its users require is access to the web and the software and data necessary to run it.
But the cloud alone can be expensive and inefficient, posing a significant risk to privacy.
The good news is that there’s another computing option that improves massively on some of the cloud’s most significant shortcomings.
That’s where Edge computing enters the scene.
Computing at the Edge entails several impressive benefits. This article explores these and compares Edge computing to computing in centralized cloud locations.
But first, let’s look at the definitions of the two computing methods.
Simply put, Edge computing is a distributed computing method that brings data storage and processing geographically closer to users.
On the other hand, cloud computing can be considered a centralized computing method. With cloud computing, data is sent to remote cloud servers that hold significant processing power and house many resources.
Before we explore the differences between these two computing methods, it’s crucial to understand Edge and cloud computing in more detail.
Edge computing brings data processing closer to users
Edge computing is distributed computing that brings computation and data storage closer to users. In Edge computing, data and applications are processed at the edge of the network, near or at the source of the data.
This can be contrasted with traditional cloud computing in which data and applications are processed centrally, often in remote data centers.
The problem with cloud computing is that data has a long way to travel before it can be effectively processed. This opens it up to security vulnerabilities and latency problems, to list just some of the concerns associated with centralized computing.
On the other hand, edge computing can help improve the performance of applications and services and reduce latency. It can also enable new types of applications and services, such as those that depend on real-time analytics and the ability to function in offline and low-connectivity environments.
Edge computing can be used in a wide variety of settings, including:
- In the home: where Edge devices such as routers, set-top boxes, and Smart Video Doorbells can provide local processing and storage for applications such as video streaming, gaming, and home security.
- In enterprise environments: where Edge servers can be deployed at branch offices and remote locations to improve the performance of mission-critical applications.
- In industrial settings: where Edge devices can be used to monitor and control machinery in real-time.
- In the Internet of Things (IoT), devices and gadgets: where devices can collect and process data from sensors and other connected devices at the Edge.
Edge computing is also a key component of the next-generation network, 5G. By bringing computation and storage closer to the point where it was initially generated, 5G can support new, demanding applications, all while offering incredibly low latency and high performance.
Cloud computing holds significant processing power and delivers a host of important services
Now, let’s turn our attention to cloud computing.
Put simply, cloud computing means storing and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of on local devices or machinery.
Interestingly, the cloud is just a metaphor for the internet. It’s a way of describing a complex infrastructure that delivers services to customers.
When you use cloud computing, you don’t have to worry about where your data is stored or how it’s backed up. The service provider takes care of that.
With cloud computing, you can access your data from any internet-connected device. You can share data and applications with others, collaborate on projects in real time, and take advantage of the cloud’s powerful processing and storage capabilities.
There are 3 main types of cloud services. These are:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the most basic type of cloud service. With IaaS, you can rent virtual machines (VMs) and other resources from a public cloud provider, using these resources to run your applications or services.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is a complete solution. With PaaS, you can develop and deploy applications on a cloud platform without worrying about managing the underlying infrastructure.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is the most comprehensive type of cloud service. With SaaS, you can use ready-made applications hosted and managed by a service provider.
Ultimately, cloud computing can be an appealing option for businesses as they don’t have to invest in their own infrastructure. Companies can also use cloud services to supplement their existing IT infrastructure.
The main difference between Edge and cloud computing
The main difference between Edge and cloud computing is that Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to users. In contrast, cloud computing relies on sending data away to centralized data centers.
Edge computing is well suited for applications that require low latency and high performance, such as video streaming and gaming. As mentioned, it can collect and process data from sensors and devices in real-time without sending this data to the cloud.
Cloud computing, on the other hand, is more flexible and scalable. It’s often used for applications that can tolerate latency, such as email and web browsing. And because data is stored in centralized data centers, it can be accessed from anywhere in the world.
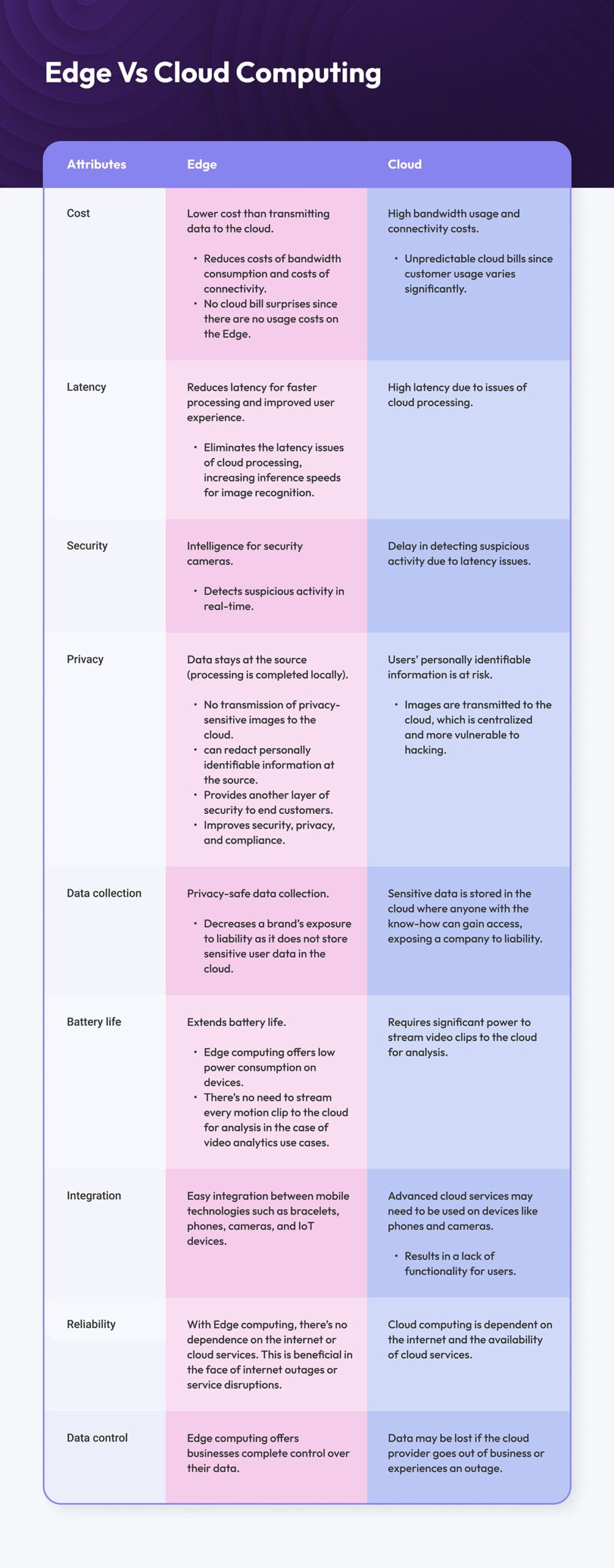
Here are some areas to consider further to understand the key differences between these two computing methods.
The advantages of cloud computing
Despite the cloud’s downfalls, businesses can enjoy numerous benefits when adopting a cloud computing strategy. These include:
1. Scalability advantages
Scaling is usually quick and easy when it comes to cloud computing. This is because cloud computing brings zero disruptions or downtime; in the case of third-party cloud services, all the infrastructure is in place. This means scaling up is as simple and quick as conducting a few additional authorizations.
2. Abundant resources
Edge computing devices often have limited resources, such as storage and processing power constraints. This can limit the types of applications that can run on them. As the cloud is a resource superpower, it’s not subjected to these same restraints and can run all kinds of processing and storage-intensive applications.
3. Great flexibility
The cloud offers businesses more flexibility compared to hosting on a local server. For example, if a company requires extra bandwidth, a cloud-based service can meet that demand instantly, rather than requiring a complex update to IT infrastructure. This flexibility can make a significant difference to the overall efficiency of an organization.
4. Less risk of data loss
The cloud’s centralized nature makes disaster recovery, data backup, and business continuity easy.
The advantages of Edge computing
Edge computing derives most of its benefits from its localized aspect. It’s this feature that, in many ways, gives Edge computing some impressive benefits over the cloud. These benefits include:
1. Decreased latency
As mentioned, Edge computing has lower latency because data is processed at the Edge (rather than in the cloud). Low latency improves user experience and can be beneficial for applications that require real-time responses, such as AR/VR, gaming, and mission-critical applications.
2. Greater cost efficiency
Edge computing can help reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud for processing. This offers improved efficiency and saves on bandwidth and connectivity costs.
3. Improved privacy and security
By keeping data local, Edge computing can help to improve privacy.
This is because data is less likely to be intercepted or hacked when it’s not transmitted over the internet.
Edge computing can also redact personally identifiable information at the source and improve compliance. It also offers effective security by detecting suspicious activity in real-time without the delay of the cloud.
4. Increased reliability
Edge computing can help to increase reliability, as there is no dependence on the internet or cloud services. This can be beneficial where there is a risk of internet outages or service disruptions.
5. More control over one’s data
When businesses use cloud computing, they rely on a third-party provider to keep their data safe and accessible. This can lead to a loss of control over one’s data. For instance, you may lose access to your data and applications if your cloud provider goes out of business or experiences an outage.
With Edge computing, on the other hand, a business will always have total control over its data.
6. Privacy safe data collection
Brands are at greater risk of exposure to liability where customer data collection is concerned. But, with Edge computing, a brand’s exposure to liability associated with stored sensitive data can be decreased when data is kept local.
7. Improved battery life
Edge computing offers low power consumption on devices. This is the case in video analytics use cases mainly because there’s no need to stream every motion clip to the cloud for analysis.
By only sending data to the cloud when necessary (if at all), Edge computing preserves battery life much longer than devices that rely on cloud computing.
Can the Edge and the cloud work together?
One of the big benefits of Edge computing is that it can complement and work seamlessly with cloud computing.
By using a mix of both Edge and cloud resources, businesses can get the best of both worlds – the flexibility and scalability of the cloud with the speed and responsiveness of Edge computing.
Using both Edge and cloud resources can have many advantages. For example, by running some applications at the Edge, a company can enjoy reduced latency for use cases that require it while still using the cloud for larger-scale computing workloads.
Edge computing is a powerful tool on its own, but when used in conjunction with cloud computing, it can be even more effective. By leveraging the strengths of both computing methods, businesses can create a more efficient, responsive, and secure IT infrastructure.
Edge computing will help meet future data processing demands
Although Edge computing is still in its early stages, it’s proving to be a game-changer for the tech industry.
By bringing computation and data storage closer to the user, Edge computing has the potential to revolutionize how we use and interact with technology.
Edge computing will become more important in the future as our reliance on technology increases.
For instance, with the proliferation of connected devices and the rise of the IoT, there will be an ever-increasing demand for quick, reliable access to data and computing resources. Edge computing will enable us to meet this demand by providing an efficient way to process and store data.
While Edge computing isn’t likely to replace cloud computing anytime soon, it does address some of the cloud’s biggest problems, making it an appealing option on its own or in a hybrid computing environment.

