Face Recognition can be useful in many different settings. Because of this, major tech firms worldwide are developing advanced Face Recognition technology.
This article explores how Edge AI enhances biometrics and discusses how moving Face Recognition to the Edge offers significant advantages.
Face Recognition and its applications
Face Recognition is a category of biometric security designed to identify and confirm/validate human faces that it finds in images and videos. This technology uses biometric software to recognize individual people’s facial features.
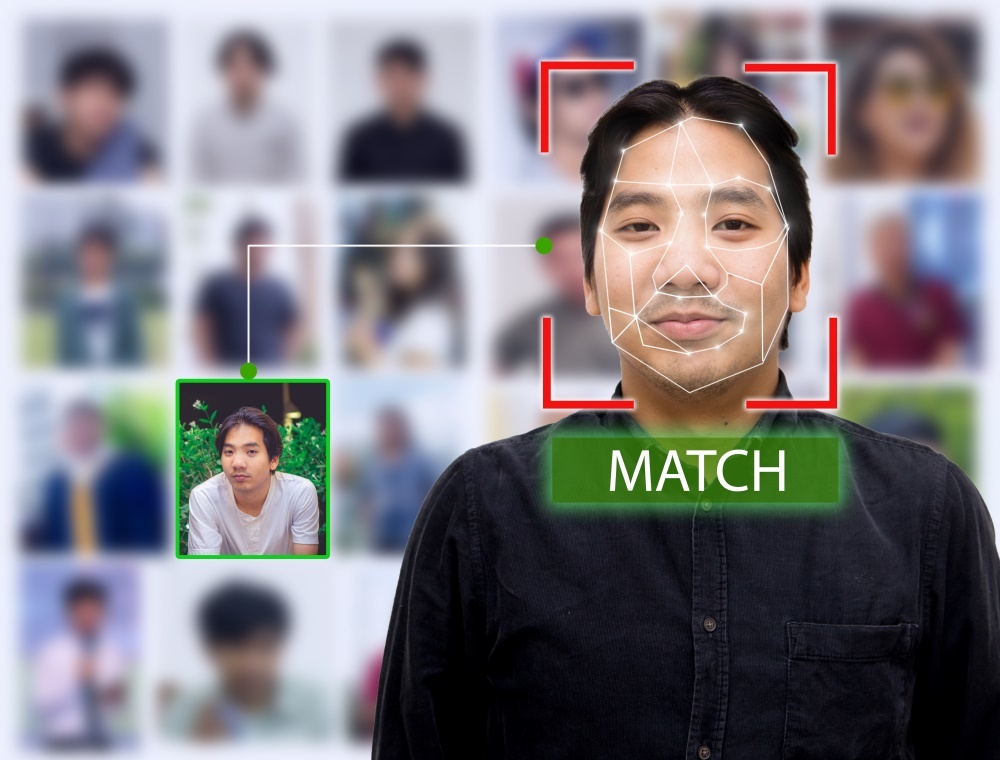
Performing Face Recognition typically involves:
Face detection
The camera detects and locates the image of a face.
Face analysis
An image of the face is captured and analyzed. The software reads the geometry of a face looking for things like the depth of one’s eye sockets and the shape of one’s cheekbones, etc.
Finding a match
The captured image of a face is then compared against a database of other known faces to see if there are any matches. If a match is found, that face is assigned an identity.
Face Recognition technology can be used to make the world safer, smarter, and more convenient. Its uses can range from allowing people to quickly and easily unlock their phones to assisting in marketing and healthcare.
On the marketing front, Face Recognition can enhance the customer experience. For instance, media companies can use Face Recognition to test audience reactions to movie trailers.
In healthcare, Face Recognition can help the patient check-in process. It can also help diagnose certain diseases and conditions and assist with staff identification and security.
These are examples of just two industries that stand to benefit from Face Recognition technology. Other industries that benefit from implementing Face Recognition include education, retail, and law enforcement.
The Edge briefly explained
Due to the tremendous growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) applications and mobile computing, billions of IoT and mobile devices are now connected to the Internet. This generates massive amounts of data.
AI solutions designed to make sense of large volumes of data are primarily cloud-based. This is because the task requires high-end hardware that can perform deep learning computing and the capacity to scale resources quickly.
Traditionally, data is transported and processed in cloud data centers, resulting in high latency, significant network bandwidth usage, privacy issues, and high costs. These issues urgently need to be solved.
To address the limitations of cloud computing, there is a need to move computing workloads closer to where data is generated.
Instead of performing computations in cloud data centers that can be thousands of miles away, Edge computing refers to computing that takes place as close to the data source as possible (even on the device itself) and doesn’t require an internet connection.
Edge computing overcomes inherent problems of the traditional cloud, such as high latency and the lack of security. Latency is significantly reduced when data doesn’t need to be sent far away for processing. While undoubtedly convenient, this can also be incredibly important, considering many computing tasks are time-sensitive.
In the case of security, Edge computing avoids sending users’ personally identifiable information to the cloud, meaning that their data stays where it’s generated and is more secure.
Edge AI is a growing subset of the overall market for artificial intelligence and provides a solution to the problems of cloud-based AI.
Edge AI remedies the shortcomings of cloud computing by using software and hardware that runs AI locally, taking advantage of the many benefits of Edge computing and opening up new opportunities for AI applications.
Edge AI enhances biometrics for better Face Recognition
According to the market research firm IDC, the worldwide Edge computing market is growing exponentially, and included in this is the expansion of Edge AI.
This growth is mainly due to the benefits of Edge computing. Specifically, moving AI for biometric applications to the Edge provides increased usability and efficiency at a low cost and enhanced privacy and security.
Edge computing will affect the experiences and information that AI delivers by changing how machines process information. For instance, the advantages of increased response times and bandwidth efficiency of running AI on (or near) devices can be critical. This is especially true when these devices are doing time-sensitive work.
In the case of a smart home security camera, the best place for data processing to occur is on the camera itself. Since there is no latency caused by sending data to the cloud, the camera can be more responsive.
Moving data processing onto devices results in higher reliability, lower latency, greater bandwidth efficiency, and better privacy than cloud computing is capable of supporting.
This is leading to a whole new class of biometrics as on-device AI will enable increasingly advanced forms of biometrics to become part of our daily lives.
What does moving to the Edge mean for Face Recognition?
Moving Face Recognition technology to the Edge comes with many benefits. But first, let’s think about what this might look like.
Deploying Face Recognition at the Edge means that the AI technology required to carry out a task is embedded within a device, e.g., a smart lock, an interactive kiosk, or a point-of-sale system. Edge devices such as these would be able to run Face Recognition quickly and with extreme precision.
Let’s explore the benefits of Edge-based Face Recognition in more detail:
- Cost of ownership
AI demands a significant amount of computing power, and cloud computing can get expensive; therefore, Edge devices have a cost advantage over the cloud. In addition to their dramatic improvements, Edge AI chips have also become cheaper over time, meaning the cost advantage is widening.
- Response time
The most successful Face Recognition algorithms can operate in mere milliseconds, and Edge-based solutions are the best to achieve this. They significantly outperform their cloud-based competitors. Speed matters because response time is critical regardless of how a business looks to use Face Recognition. For example, not identifying banned individuals quickly enough could cause tremendous harm to a company.
- Service availability
Unfortunately, no internet service is immune from the occasional low-bandwidth issue or interruption. As Edge-based Face Recognition doesn’t require an internet connection, it’s not vulnerable to these issues. Imagine if the door lock to your home or business didn’t work because it relied on cloud-based Face Recognition!
- Detection/activation
Traditional Face Recognition technology quickly processes video feeds looking for visible faces. It then sends those results back to the client. Continuously moving video around a network uses a lot of bandwidth. With Edge AI, on the other hand, cameras record footage selectively and send only footage that contains a face. This dramatically reduces the amount of data that’s recorded and transmitted, translating into lower operational costs and lower bandwidth use compared to traditional server-side processing.
- Industrial design
Edge AI runs on low power. By extension, it also has a reduced weight and size. This allows product designers to develop innovative design options that can better suit specific environments and architectural limitations.
The Future of Face Recognition Technology
As can be seen, Face Recognition at the Edge empowers and supports users in significant ways. Edge technology has already begun to facilitate the adoption of highly advanced Face Recognition, which is only going to increase in the future.
Xailient Face Recognition is part of this future due to its incredible accuracy and efficiency at the Edge.

